How to Use FFmpeg for Live Streaming: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you’ve ever wanted to stream live video from your computer to the internet like a pro—without expensive software—then let me introduce you to your new best friend: FFmpeg. Yes, that same FFmpeg we used to curse while building YouTube clones back in 2007 is still alive and kicking… and guess what? It’s great for…

FFmpeg and the Rise (and Fall) of the YouTube Clones: A Love-Hate Story from the Hosting Trenches
Let me take you on a little trip down memory lane—back to the early 2000s, a time when flip phones were king, MySpace ruled the internet, and YouTube was still the new kid on the block. Around 2007, something amazing (and slightly chaotic) happened in the web hosting world: ? Everyone wanted to build their…
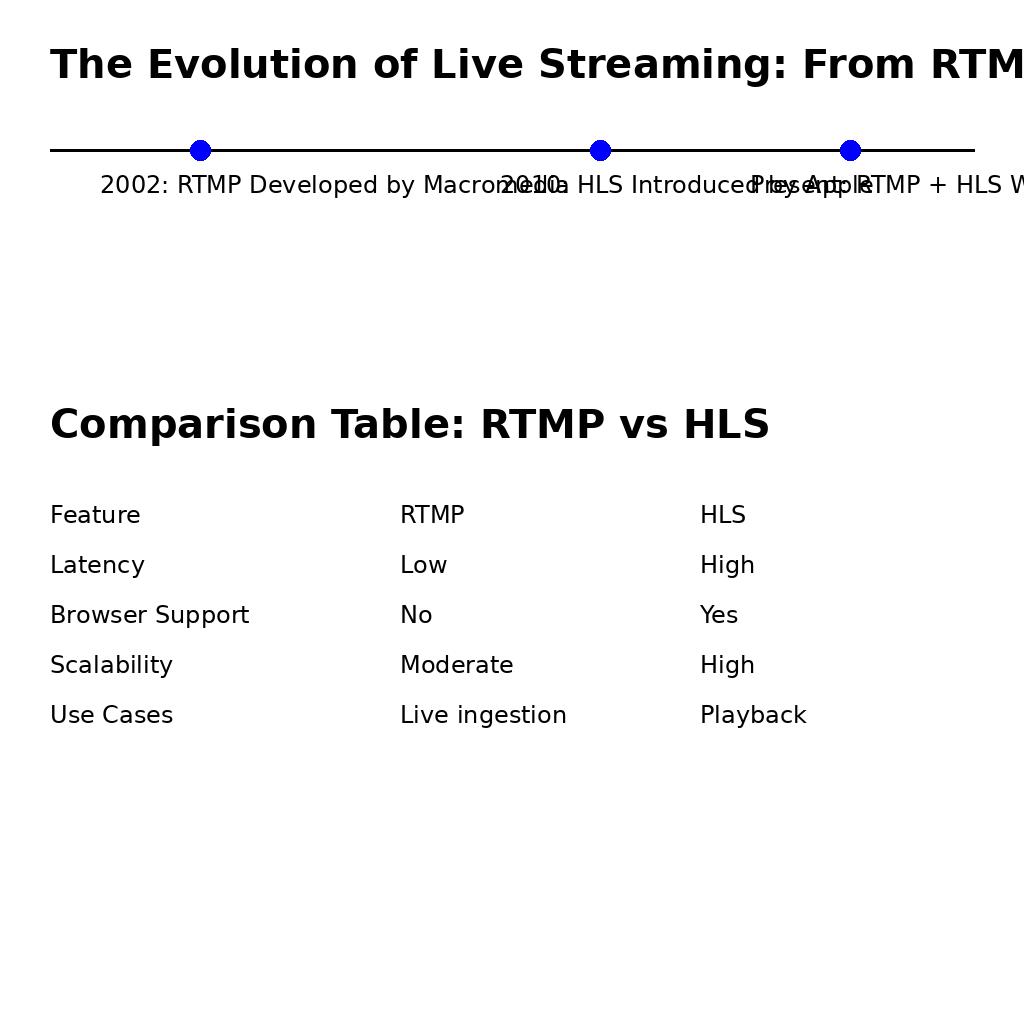
Choosing Between NGINX and Wowza for RTMP Streaming
Choosing Between NGINX and Wowza for RTMP Streaming When building a live streaming workflow, selecting the right tools for managing RTMP and HLS workflows is crucial. Two popular choices for handling RTMP ingestion and HLS conversion are NGINX and Wowza. Both have their strengths and cater to different needs, but which one is right for…
HOW DO I PREVIEW MY RTMP STREAM?
Before moving any video source or graphic overlay to your recording or stream, you usually evaluate it in the preview window. Before broadcasting or distributing your content, previewing RTMP streams is a crucial step in assuring the caliber and accuracy of your streaming setup. Before broadcasting or publishing your content, checking the RTMP stream’s compatibility,…
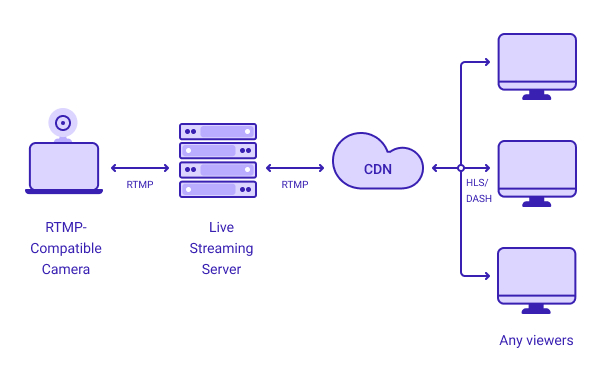
WHAT IS AN RTMP SERVER, AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
An open-source protocol called Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP), which Adobe owns is made for streaming audio and video while preserving low-latency connections. The RTMP protocol broadcasts data, audio, and video across the internet. A server that uses the RTMP protocol to control the streaming of audio and video content from a source to one or…